Intermittent Stabilization Anchor Systems
Why is stabilization needed?
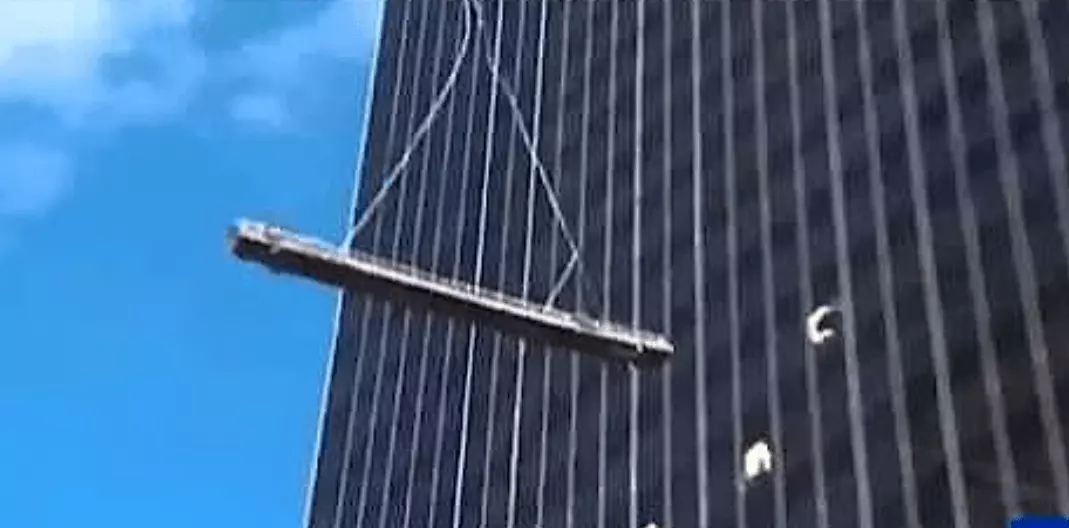
Generally, stabilization is intended to keep workers suspended on platforms from swaying due to the effects of wind and to help with work positioning.
See how suspended platforms may perform when no stabilization is used in the video. (Click on the image or the link below.)
Is stabilization required?
Stabilization in some form is required for most suspended work.
Safety from the top down.
CLICK HERE to Request FREE Design.
Roof Rigging with Intermittent Stabilization.
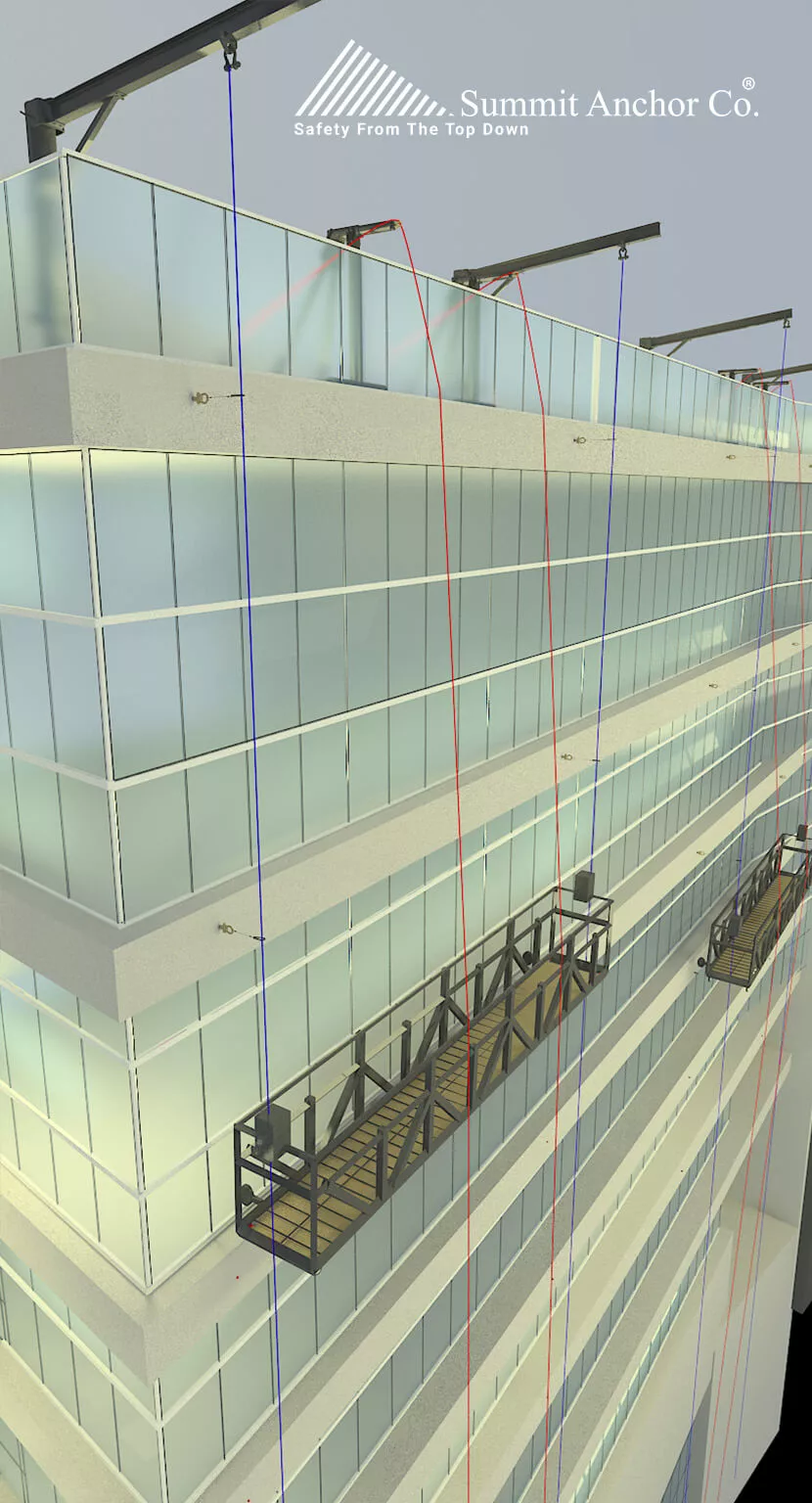
How does an intermittent stabilization system for roof rigged platforms work?
Systems designed with intermittent stabilization anchors are intended for roof rigging of suspended platforms to prevent workers from swaying which may result in damage to the building façade and danger to the suspended workers.
- The minimum design placement requirements for intermittent stabilization anchor systems for roof rigging suspended platforms are to locate the anchors in vertical rows at every third floor or 50 feet (15.3 m), whichever is less. The ISAs must be located in-line with the intended suspension point of the wire ropes of the platform. If ISAs are offset, either inboard or outboard of the intended suspension point of the platform, they must both be offset either inboard or outboard of the suspension cables of the platform. For the stabilization system to function best with a 2-point suspended platform, locate the ISAs in pairs horizontally level and perpendicular to each of the suspension cables of the platform.
- As the suspended platform descends past the elevation of each anchor, each of the two workers will secure a “quick connect – disconnect pin” tethered from the suspension wire rope of the suspended platform to the ISA. Each stabilizer-pin will be configured with an adjustable lanyard attached to the suspension wire rope(s). The lanyard will be taut making the suspension rope angulate to a force of at least 10 lbs. of the platform’s building face rollers against the building. This process will be repeated at each ISA Accept Change elevation during the descent of the platform from the roof. The stabilization pin-lanyard assembly will generally be left in place as the platform descends to the lowest work level.
- Then, during the platform’s ascent to the roof, the above process will be reversed, that is, the pin-lanyard assembly will be removed at each elevation as the ISAs are reached.
- The minimum loading capacity requirements for intermittent stabilization anchors, “shall be capable of sustaining without failure at least 4 times the maximum anticipated load to be applied or transmitted to the anchors. The ultimate design load for each anchor shall be a minimum of 600lb, which includes a safety factor of 4, applied laterally or [and] (added for clarification by Summit Anchor) perpendicularly but not simultaneously.” Excerpt from the A120.1 2021.
![Roof Launch ISA 3EA FLOORS 11-14 [ISA Bigger] L Roof Launch ISA 3EA FLOORS 11-14 [ISA Bigger] L](https://summitanchor.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Roof-Launch-ISA-3EA-FLOORS-11-14-ISA-Bigger-L.webp)
Safety from the top down.
CLICK HERE to Request FREE Design.
Roof Rigging with Intermittent Stabilization.
How does workstation stabilization for ground rigging work?
Systems designed with Workstation Stabilization Anchors are typically used for ground rigging of platforms to prevent swaying at each working level, as required by OSHA. See link to OSHA’s interpretation letter for ground rigged platforms for clarification.
https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/standardinterpretations/1987-07-16
- The minimum design requirements for placement of workstation stabilization anchor systems are to locate the anchors in vertical rows at each working level. The work station anchors (also known as ISAs for the purpose of this manual) must be located in-line with the intended suspension point of the wire ropes of the platform. If ISAs are offset, either inboard or outboard of the intended suspension point of the platform, they must both be offset either inboard or outboard of the suspension cables of the platform. For the stabilization system to function best with a 2-point suspended platform, locate the ISAs in pairs horizontally level and perpendicular to each of the suspension cables of the platform.
- As the suspended platform ascends to just below the elevation of each anchor, each of the two workers will secure a “quick connect – disconnect pin” tethered from the suspension wire rope of the suspended platform to the building’s tie-in anchor. Each stabilizer-pin will be configured with an adjustable lanyard attached to the suspension wire rope(s). The lanyard will be taut, making the suspension rope angulate to a force of at least 10 lbs. of the platform’s building face rollers against the building.
- When workers are ready to ascend to the next workstation, the “stabilization pin-lanyard assembly” will be removed then reconnected at each work elevation at each workstation at the building’s tie-in anchor.
- The minimum loading capacity requirements for intermittent stabilization anchors, “shall be capable of sustaining without failure at least 4 times the maximum anticipated load to be applied or transmitted to the anchors. The ultimate design load for each anchor shall be a minimum of 600lb, which includes a safety factor of 4, applied laterally or [and] (added for clarification by Summit Anchor) perpendicularly but not simultaneously.” Excerpt from the A120.1 2021.

Safety from the top down.
CLICK HERE to Request FREE Design.
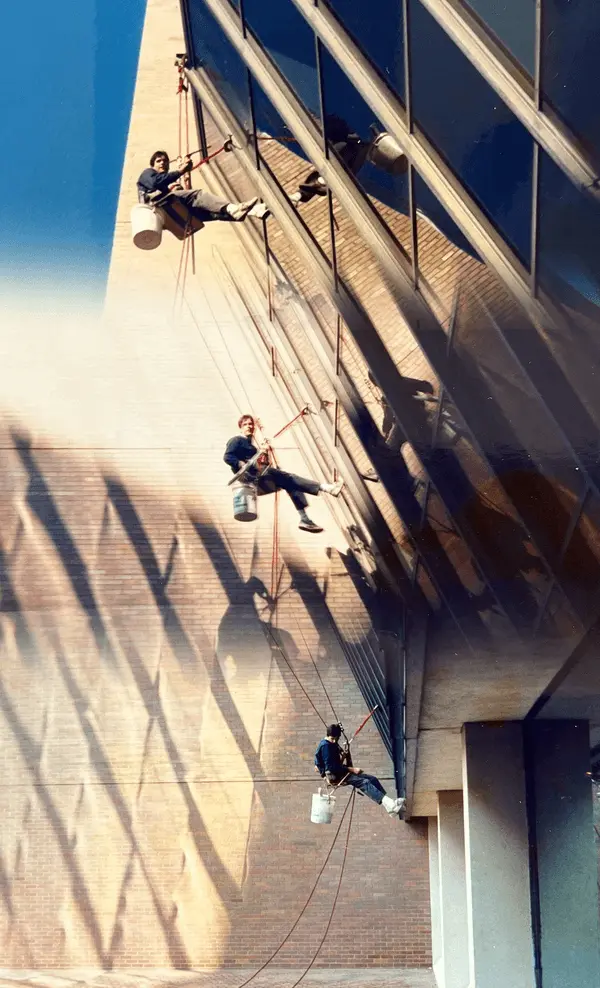
Stabilization for Rope Descent Systems.
How do stabilization systems work for rope descent systems?
RDS Stabilization includes such options as rope angulation, suction cups, and track systems. OSHA requires “stabilization at the specific work location when descents are greater than 130 feet.” OSHA has also determined that workstation stabilization can be something as simple as a suction cup. It is very common for window cleaners to roof rig using RDS. Then, as the worker descends, he/she attaches a suction cup to a window at each workstation to stabilize and to prevent the worker from swaying due to the effects of wind.
See link to OHSA hearing:
https://summitanchor.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Pages-85-86-87.pdf
Stabilization can be a permanent solution such as a rail, track system, or mullion track system. These permanent, continuous stabilization systems can provide greater protection from swaying than suction cups which can only be used on smooth surfaces like glass.

Safety from the top down.
CLICK HERE to Request FREE Design.